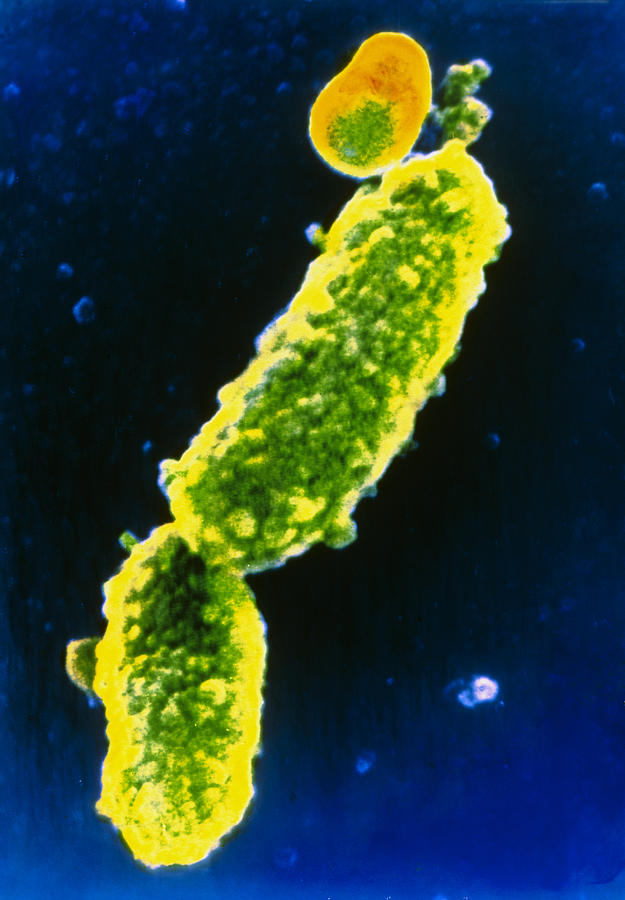
Background "Whooping cough". The "whoop" is caused on inspiration between coughs. Most common in kids < 1yo, because they haven't completed the whole vaccine series, AND adults, who have waning immunity. One of the only vaccine preventable diseases that has increased in prevalence recently
Whooping cough (/ ˈ h uː p ɪ ŋ / or / ˈ w uː p ɪ ŋ /), also known as pertussis or the 100-day cough, is a highly contagious, vaccine-preventable bacterial disease. [1] [10] Initial symptoms are usually similar to those of the common cold with a runny nose, fever, and mild cough, but these are followed by two or three months of severe coughing fits. [1]
Recent trends. Reports of pertussis cases were lower than usual over the past few years, during and following the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the United States is beginning to return to pre-pandemic patterns where more than 10,000 cases are typically reported each year. It's likely mitigation measures used during the pandemic (e.g., masking, remote learning) lowered transmission of pertussis.
Whooping cough, also called pertussis, is a serious respiratory infection caused by a type of bacteria called Bordetella pertussis.The infection causes violent, uncontrollable coughing that can
How Whooping Cough Symptoms Compare. Whooping cough vs. croup. Whooping cough is similar to croup in that both illnesses are infections affecting the respiratory tract, the system related to
Whooping cough (/ ˈ h uː p ɪ ŋ / or / ˈ w uː p ɪ ŋ /), also known as pertussis or the 100-day cough, is a highly contagious, vaccine-preventable bacterial disease. [1] [10] Initial symptoms are usually similar to those of the common cold with a runny nose, fever, and mild cough, but these are followed by two or three months of severe coughing fits. [1] Recent trends. Reports of pertussis cases were lower than usual over the past few years, during and following the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the United States is beginning to return to pre-pandemic patterns where more than 10,000 cases are typically reported each year.
It's likely mitigation measures used during the pandemic (e.g., masking, remote learning) lowered transmission of pertussis. Whooping cough, also called pertussis, is a serious respiratory infection caused by a type of bacteria called Bordetella pertussis.The infection causes violent, uncontrollable coughing that can How Whooping Cough Symptoms Compare. Whooping cough vs. croup. Whooping cough is similar to croup in that both illnesses are infections affecting the respiratory tract, the system related to
Pertussis, often called whooping cough, is caused by a bacterial infection. It's a highly contagious illness that spreads easily from person to person through airborne germs from the nose and
CDC recommends whooping cough (pertussis) vaccination for everyone. Whooping cough vaccines are the best way to protect against whooping cough.
What is whooping cough (pertussis)? Whooping cough, or pertussis, is very contagious and mainly affects infants and young children. Whooping cough is caused by a bacterium called Bordetella pertussis.The illness is characterized by coughing spells that end with a characteristic "whoop" as air is inhaled.
Whooping cough (pertussis) is a respiratory infection that causes severe coughing fits for many weeks. Treatment with antibiotics can limit the spread to others.
Whooping Cough (Pertussis) Symptoms & Treatment - Cleveland Clinic
Pertussis, often called whooping cough, is caused by a bacterial infection. It's a highly contagious illness that spreads easily from person to person through airborne germs from the nose and CDC recommends whooping cough (pertussis) vaccination for everyone. Whooping cough vaccines are the best way to protect against whooping cough. What is whooping cough (pertussis)? Whooping cough, or pertussis, is very contagious and mainly affects infants and young children.
Whooping cough is caused by a bacterium called Bordetella pertussis.The illness is characterized by coughing spells that end with a characteristic "whoop" as air is inhaled. Whooping cough (pertussis) is a respiratory infection that causes severe coughing fits for many weeks. Treatment with antibiotics can limit the spread to others.
Pertussis is the second most frequently notified vaccine preventable disease in Australia. 64 Despite a longstanding pertussis immunisation program, and a substantial decline in morbidity and mortality from the disease, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic pertussis outbreaks occurred every few years. 65
Pertussis can also present as a non-specific persistent cough; Vomiting often follows a coughing spasm; Infants may develop apnoea and/or cyanosis with coughing spasms; Close contact with a case of Pertussis may raise suspicion Other family members frequently have a cough (>70% of household contacts are also infected) Examination
Pertussis, or whooping cough, is an acute respiratory tract infection that continues to affect a significant portion of the global population, with more than 24 million estimated cases in 1
Whooping cough (also called pertussis or the "100-day cough") is a respiratory infection known for the high-pitched "whoop" sound some people make after coughing. Pertussis affects people of all ages but usually causes the most severe symptoms in infants.
Whooping Cough (Pertussis) Symptoms & Treatment - Cleveland Clinic
Pertussis is the second most frequently notified vaccine preventable disease in Australia. 64 Despite a longstanding pertussis immunisation program, and a substantial decline in morbidity and mortality from the disease, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic pertussis outbreaks occurred every few years. 65 Pertussis can also present as a non-specific persistent cough; Vomiting often follows a coughing spasm; Infants may develop apnoea and/or cyanosis with coughing spasms; Close contact with a case of Pertussis may raise suspicion Other family members frequently have a cough (>70% of household contacts are also infected) Examination Pertussis, or whooping cough, is an acute respiratory tract infection that continues to affect a significant portion of the global population, with more than 24 million estimated cases in 1 Whooping cough (also called pertussis or the "100-day cough") is a respiratory infection known for the high-pitched "whoop" sound some people make after coughing. Pertussis affects people of all ages but usually causes the most severe symptoms in infants.
Pertussis: What you need to know Pertussis is a highly infectious respiratory tract infection. It is characterized by a "hacking" cough, followed by a high pitched intake of breath, or a "whoop" (hence the common
Pertussis (whooping cough) is a respiratory tract infection characterized by a paroxysmal cough. The most common causative organism is Bordetella pertussis (see the image below), though Bordetella parapertussis also has been associated with this condition in humans.Pertussis remains a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in infants younger than 2 years.
Whooping cough (pertussis) is a highly contagious respiratory disease caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. People with whooping cough can have severe coughing fits. The cough can linger for weeks or even months. Vaccination is the best way to prevent whooping cough. Why it matters to public health
Clinical Features. Pertussis is highly contagious; secondary attack rates exceed 80% in susceptible household contacts 19 20.The incubation period is usually 5 to 10 days, but symptoms may develop up to 3 weeks after exposure 21.The clinical course of pertussis infection has 3 stages: catarrhal, paroxysmal, and convalescent.
Pertussis | Infection Control | CDC
Pertussis: What you need to know Pertussis is a highly infectious respiratory tract infection. It is characterized by a "hacking" cough, followed by a high pitched intake of breath, or a "whoop" (hence the common Pertussis (whooping cough) is a respiratory tract infection characterized by a paroxysmal cough. The most common causative organism is Bordetella pertussis (see the image below), though Bordetella parapertussis also has been associated with this condition in humans.Pertussis remains a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in infants younger than 2 years. Whooping cough (pertussis) is a highly contagious respiratory disease caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. People with whooping cough can have severe coughing fits.
The cough can linger for weeks or even months. Vaccination is the best way to prevent whooping cough. Why it matters to public health Clinical Features. Pertussis is highly contagious; secondary attack rates exceed 80% in susceptible household contacts 19 20.The incubation period is usually 5 to 10 days, but symptoms may develop up to 3 weeks after exposure 21.The clinical course of pertussis infection has 3 stages: catarrhal, paroxysmal, and convalescent.
Whooping cough is a serious respiratory infection. It is caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. It is also called pertussis. Whooping cough is very infectious and spreads easily from one person to another. It affects people of all ages and can be life-threatening in babies.
Pertussis, or the 'hundred-day cough', are other names for whooping cough. Whooping cough can feel uncomfortable and last for a long time. After 1 to 2 weeks, the cold-like symptoms get better, but the cough gets worse. After 2 to 6 weeks, the cough begins to get better. But it can take weeks to months for the cough to go away completely.
Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. In 2018, there were more than 151 000 cases of pertussis globally. Pertussis spreads easily from person to person mainly through droplets produced by coughing or sneezing. The disease is most dangerous in infants
Pertussis (whooping cough) is common in the United States, with frequent outbreaks. Protecting people at highest risk of serious illness is the primary focus during outbreaks.
About Whooping Cough Outbreaks | Whooping Cough | CDC
Whooping cough is a serious respiratory infection. It is caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. It is also called pertussis. Whooping cough is very infectious and spreads easily from one person to another. It affects people of all ages and can be life-threatening in babies.
Pertussis, or the 'hundred-day cough', are other names for whooping cough. Whooping cough can feel uncomfortable and last for a long time. After 1 to 2 weeks, the cold-like symptoms get better, but the cough gets worse. After 2 to 6 weeks, the cough begins to get better. But it can take weeks to months for the cough to go away completely.
Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. In 2018, there were more than 151 000 cases of pertussis globally. Pertussis spreads easily from person to person mainly through droplets produced by coughing or sneezing. The disease is most dangerous in infants Pertussis (whooping cough) is common in the United States, with frequent outbreaks. Protecting people at highest risk of serious illness is the primary focus during outbreaks.
Pertussis remains one of the leading causes of vaccine-preventable deaths worldwide. Whooping Cough Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, can cause serious illness in people of all ages but is most dangerous for babies.
Whooping cough (also known as pertussis) is a bacterial infection that causes long stretches of severe coughs that sometimes end with a whooping sound.
Whooping cough is a bacterial infection caused by Bordetella pertussis. It spreads when an infected person coughs or sneezes and you breathe it in. The bacteria affect the lungs and airways, causing a person to cough violently and uncontrollably. This can make it hard for the infected person to breathe.
Clinical features. Pertussis has an insidious onset with catarrhal symptoms that are indistinguishable from those of minor respiratory tract infections Next is the paroxysmal stage characterized by numerous, rapid coughs The final stage is the convalescent stage, which can take from weeks to months to resolve.
Clinical Overview of Pertussis | Whooping Cough | CDC
Pertussis remains one of the leading causes of vaccine-preventable deaths worldwide. Whooping Cough Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, can cause serious illness in people of all ages but is most dangerous for babies. Whooping cough (also known as pertussis) is a bacterial infection that causes long stretches of severe coughs that sometimes end with a whooping sound. Whooping cough is a bacterial infection caused by Bordetella pertussis. It spreads when an infected person coughs or sneezes and you breathe it in.
The bacteria affect the lungs and airways, causing a person to cough violently and uncontrollably. This can make it hard for the infected person to breathe. Clinical features. Pertussis has an insidious onset with catarrhal symptoms that are indistinguishable from those of minor respiratory tract infections Next is the paroxysmal stage characterized by numerous, rapid coughs The final stage is the convalescent stage, which can take from weeks to months to resolve.