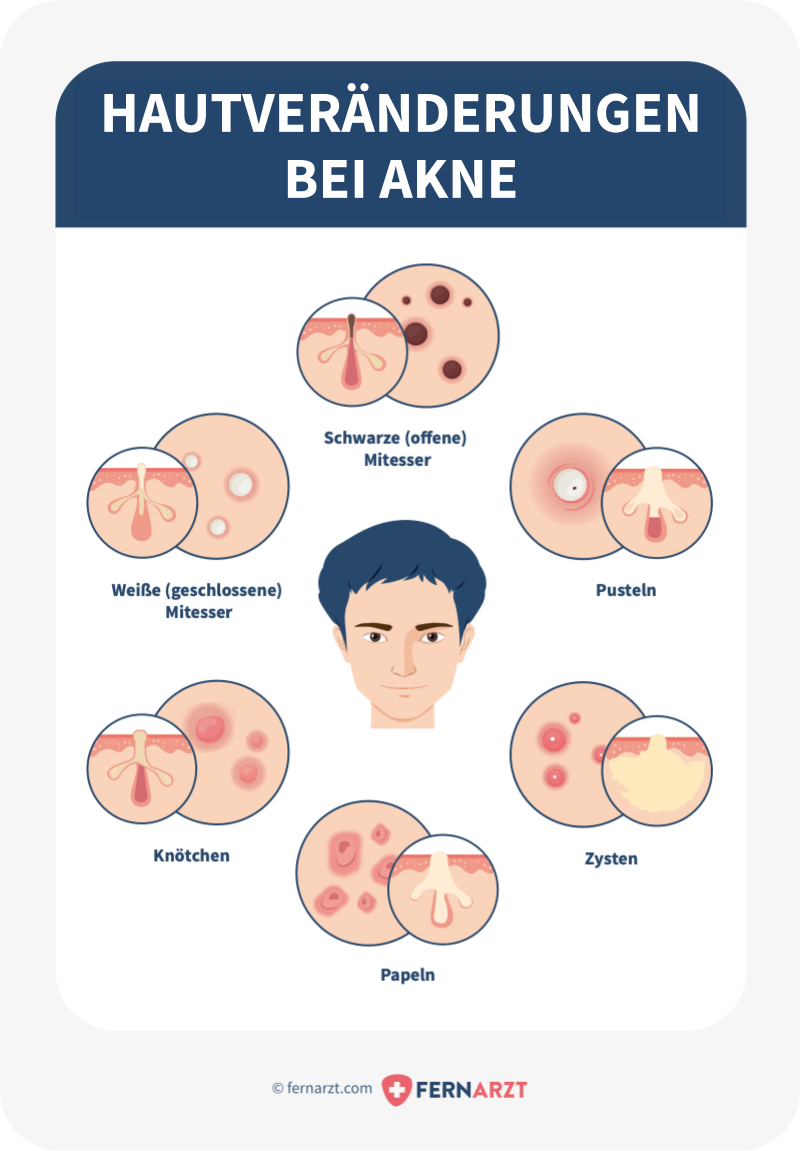
Die Akne papulopustulosa ist eine von mehreren möglichen Erscheinungsformen der Akne vulgaris (der gewöhnlichen Akne). Beinahe 80 Prozent aller Menschen leiden irgendwann in ihrem Leben an einer Akne. Leichte „Mitesser", schwarze Pünktchen auf und um Nase und Kinn, werden als Acne comedonica bezeichnet.
Papulopustular rosacea has many of the same symptoms regular rosacea does. "The skin is extra sensitive and overreactive to the environment, and you may develop redness and flush easily, in
Papulopustular rosacea is characterized by pustules similar to acne, read on for prevention tips, treatment options to discuss with your doctor, and home remedies.
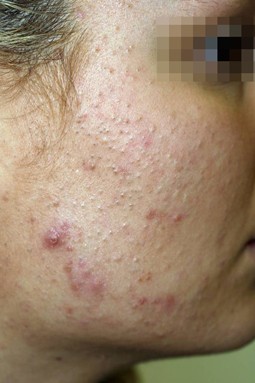
Acne papules are small, inflamed bumps caused by excess oil in your skin, bacteria, hormones and some medications. They don't have a pus-filled tip like other forms of acne.
Erfahre, was die Akne papulopustulosa ist, wie sie sich auszeichnet und welche Faktoren sie auslösen können. Lese, wie Du sie erkennen und behandeln kannst, und wie Du eine Online-Diagnose und Therapieempfehlung per App erhalten kannst.
Papulopustular rosacea has many of the same symptoms regular rosacea does. "The skin is extra sensitive and overreactive to the environment, and you may develop redness and flush easily, in Papulopustular rosacea is characterized by pustules similar to acne, read on for prevention tips, treatment options to discuss with your doctor, and home remedies. Acne papules are small, inflamed bumps caused by excess oil in your skin, bacteria, hormones and some medications. They don't have a pus-filled tip like other forms of acne. Erfahre, was die Akne papulopustulosa ist, wie sie sich auszeichnet und welche Faktoren sie auslösen können.
Lese, wie Du sie erkennen und behandeln kannst, und wie Du eine Online-Diagnose und Therapieempfehlung per App erhalten kannst.
Die Acne papulopustulosa ist eine durch sekundäre Entzündung von Komedonen gekennzeichnete Verlaufsform der Acne vulgaris. Symptomatik. Charakteristisch ist die auf die Komedonenbildung folgende Entzündung und Ausbildung von Papeln und Pusteln. Schwere Entzündungen können tiefsitzende knotige Defekte hinterlassen.
Fluhr JW et al (1999) In Vitro activity of 6 antimicrobials against propionibacteria isolates from untreated acne papulopustulosa. Central blood bacteriol 289: 53-61; Gollnick H, Schramm M (1998) Topical drug treatment in acne. Dermatology 196: 119-125; Gollnick H (2002) Acne and its subtypes. dermatologist 53: 322-327
Today in Things That Look Like Acne But Aren't, let's take a closer look at something called papulopustular rosacea (wow, so beautiful, so majestic, so rolls-off-the-tongue!).
Papulopustular rosacea, also known as acne rosacea, is one of the more common sub-types of rosacea. We spoke to dermatologists about how to tell difference between acne rosacea and typical acne or
Papulopustular Rosacea: When Acne and Rosacea Combine - Allure
Die Acne papulopustulosa ist eine durch sekundäre Entzündung von Komedonen gekennzeichnete Verlaufsform der Acne vulgaris. Symptomatik. Charakteristisch ist die auf die Komedonenbildung folgende Entzündung und Ausbildung von Papeln und Pusteln. Schwere Entzündungen können tiefsitzende knotige Defekte hinterlassen. Fluhr JW et al (1999) In Vitro activity of 6 antimicrobials against propionibacteria isolates from untreated acne papulopustulosa.
Central blood bacteriol 289: 53-61; Gollnick H, Schramm M (1998) Topical drug treatment in acne. Dermatology 196: 119-125; Gollnick H (2002) Acne and its subtypes. dermatologist 53: 322-327 Today in Things That Look Like Acne But Aren't, let's take a closer look at something called papulopustular rosacea (wow, so beautiful, so majestic, so rolls-off-the-tongue!). Papulopustular rosacea, also known as acne rosacea, is one of the more common sub-types of rosacea. We spoke to dermatologists about how to tell difference between acne rosacea and typical acne or
Acne Papulopustulosa (Papulopustular Acne) Chapter; pp 263-269; Cite this chapter; Download book PDF. ACNE and ROSACEA. Acne Papulopustulosa (Papulopustular Acne) Download book PDF. Gerd Plewig Prof. Dr. 3 & Albert M. Kligman M.D., Ph.D. 4